| Main » Articles » About Baltic Amber |
| Entries in category: 17 Shown entries: 1-10 |
Pages: 1 2 » |
Sort by: Name
 In ancient Rome amber
was used as medicine and as a protection against different diseases.
Calistratus, the famous physician of those times, wrote that amber
protects from madness, powder of amber mixed with honey cures throat,
ear and eye diseases, and taken with water cures stomach illnesses. In ancient Rome amber
was used as medicine and as a protection against different diseases.
Calistratus, the famous physician of those times, wrote that amber
protects from madness, powder of amber mixed with honey cures throat,
ear and eye diseases, and taken with water cures stomach illnesses. |
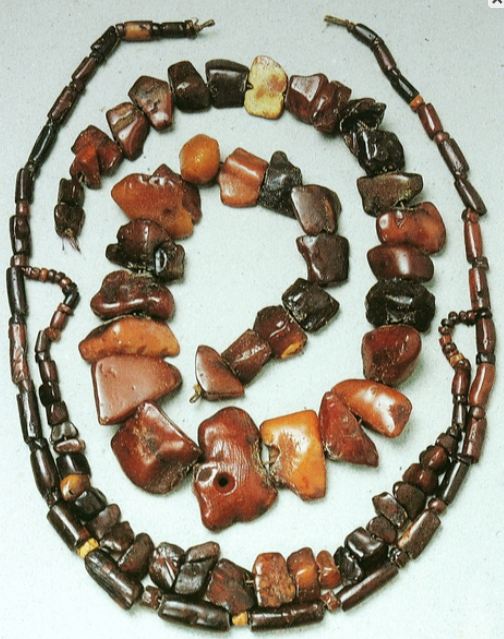
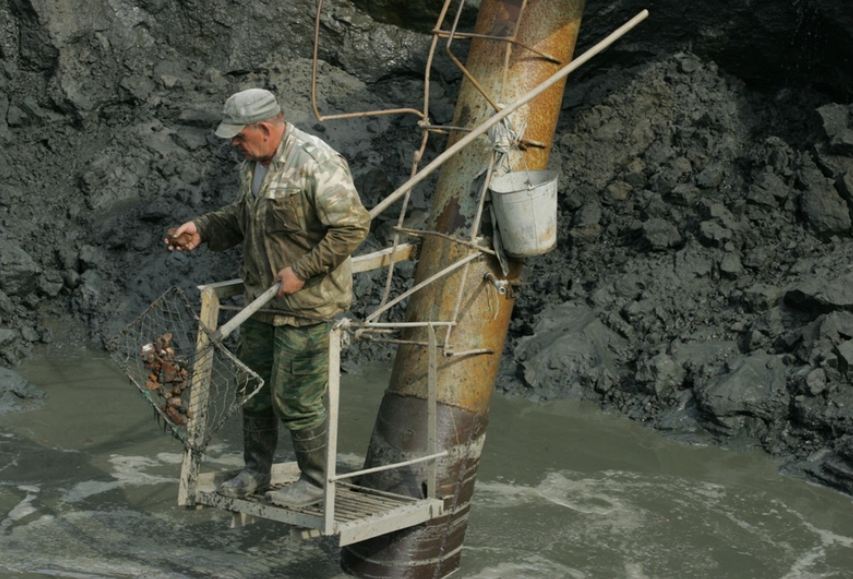
 Juodkrantė’s Treasure story started in the middle of the 19th
century, a lot of amber was found after some navigation works in the
Curonian Lagoon near Juodkrantė. Rumours had been spread about enormous
amber resources on the bed of the Curonian Lagoon. In 1857 two famous
merchants of Klaipėda Wilhelm Stantien and Moritz Becker established a
company: "Stantien and Becker". Juodkrantė’s Treasure story started in the middle of the 19th
century, a lot of amber was found after some navigation works in the
Curonian Lagoon near Juodkrantė. Rumours had been spread about enormous
amber resources on the bed of the Curonian Lagoon. In 1857 two famous
merchants of Klaipėda Wilhelm Stantien and Moritz Becker established a
company: "Stantien and Becker". |
 More than one location on the coast of the Baltic
Sea keeps the layers of amber but they are deep underground. A
primitive was able to learn about amber only when nature itself had
opened up its secrets. In Schleswig Holstein, in undermined amber
layers, people began to collect this nice mineral and make a variety of
ornaments and figures of it in middle Stone Age. However, these reserves
were too little. More than one location on the coast of the Baltic
Sea keeps the layers of amber but they are deep underground. A
primitive was able to learn about amber only when nature itself had
opened up its secrets. In Schleswig Holstein, in undermined amber
layers, people began to collect this nice mineral and make a variety of
ornaments and figures of it in middle Stone Age. However, these reserves
were too little. |
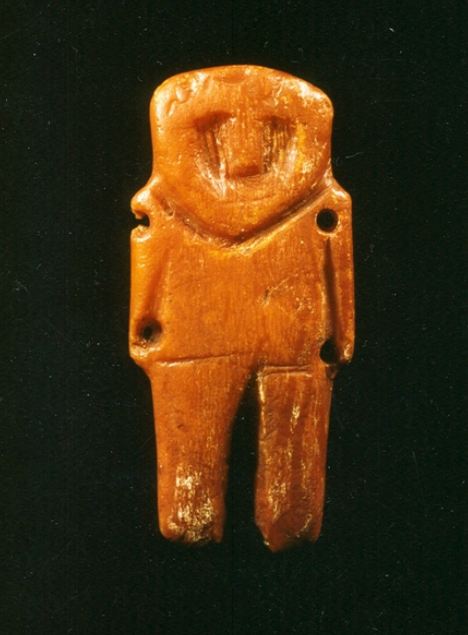
 6000 year old traditions show amber prevalence and respect of people, who lived on the Baltic Sea coast (Lithuania and the Kaliningrad
area). At first these traditions were created by ancient inhabitants of
the Baltic coast, and Balts since 2000-1800 BC. In Lithuania
the oldest findings of amber are of Neolithic period (4000-1600 BC).
Neolithic amber jewellery - pendants, beads, buttons, amulets - were
discovered in the former settlements near the Baltic Sea (Curonian Spit,
Palanga, Šventoji and Prussia). 6000 year old traditions show amber prevalence and respect of people, who lived on the Baltic Sea coast (Lithuania and the Kaliningrad
area). At first these traditions were created by ancient inhabitants of
the Baltic coast, and Balts since 2000-1800 BC. In Lithuania
the oldest findings of amber are of Neolithic period (4000-1600 BC).
Neolithic amber jewellery - pendants, beads, buttons, amulets - were
discovered in the former settlements near the Baltic Sea (Curonian Spit,
Palanga, Šventoji and Prussia). |
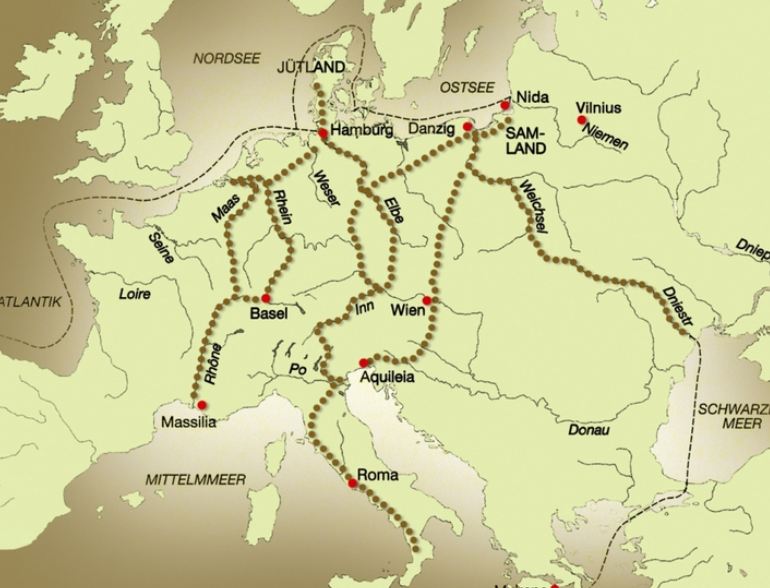 In the Baltic lands amber trade began in Neolithic period. Amber spread
from the main centres of its extraction from Jutland and eastern Baltic
countries, including Lithuania, to the Central, Eastern Europe and even reaching Egypt. German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann during the digging in Troy with many other things found amber beads in 1871-1890. Scientists determined that the article came from the shores of the Baltic
Sea 3000 years ago. This archaeologist found Baltic amber when dug
Mycenaean domed graves which were poured in about 1600-800 BC. In the Baltic lands amber trade began in Neolithic period. Amber spread
from the main centres of its extraction from Jutland and eastern Baltic
countries, including Lithuania, to the Central, Eastern Europe and even reaching Egypt. German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann during the digging in Troy with many other things found amber beads in 1871-1890. Scientists determined that the article came from the shores of the Baltic
Sea 3000 years ago. This archaeologist found Baltic amber when dug
Mycenaean domed graves which were poured in about 1600-800 BC. |
 Amber (or succinite) is a fossil pine (Pinus succinifera) resin that has
achieved a stable state through oxidation, influence of micro-organisms
and other processes. Taking into consideration chemical features, resin
is a mixture of organic compounds and is assigned to the class of
terpenes. Resin isn’t soluble in water, has a specific smell, and is
sticky in the beginning. Resin had lots of terpenes, which prevented
from crystallizing. But terpenes evaporated and resin hardened, oxidized
and isomerated. Amber (or succinite) is a fossil pine (Pinus succinifera) resin that has
achieved a stable state through oxidation, influence of micro-organisms
and other processes. Taking into consideration chemical features, resin
is a mixture of organic compounds and is assigned to the class of
terpenes. Resin isn’t soluble in water, has a specific smell, and is
sticky in the beginning. Resin had lots of terpenes, which prevented
from crystallizing. But terpenes evaporated and resin hardened, oxidized
and isomerated. |
 "Only the amber, rubbed and warmed up by hands, attracting mustard seeds is considered to be real.” (Tao Chuncinas 452-536) |
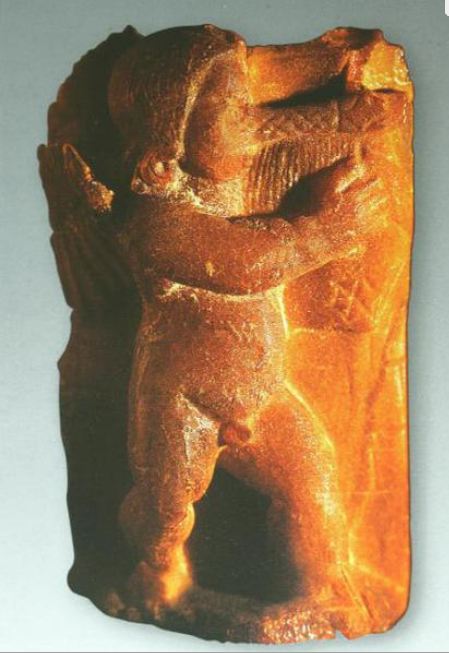 We can only guess when people started using amber as jewellery or amulet
raw material giving it magical meaning. It is known that it was treated
with flint knives, cutters, scrapers, burr grinding stone and sand. The
oldest known amber article was created at the end of the Old Stone Age
(8 chiliad BC). It was an amber plate found in reindeer hunting camp
near Hamburg. Ancient
amber is rich in examples of art in many European museums. They possess
amber of each period of the history beginning with the Neolithic and
ending today, ornaments and other articles show a great popularity of
amber and its wide usage in applied decorative arts. We can only guess when people started using amber as jewellery or amulet
raw material giving it magical meaning. It is known that it was treated
with flint knives, cutters, scrapers, burr grinding stone and sand. The
oldest known amber article was created at the end of the Old Stone Age
(8 chiliad BC). It was an amber plate found in reindeer hunting camp
near Hamburg. Ancient
amber is rich in examples of art in many European museums. They possess
amber of each period of the history beginning with the Neolithic and
ending today, ornaments and other articles show a great popularity of
amber and its wide usage in applied decorative arts. |
 Amber is mentioned even in the 10th century BC in Assyrian cuneiform. It says that in the sea, where Northern winds are changing (Persian
Gulf), his (king’s) merchants gather pearls, and in the sea, where
Northern Star shines (Baltic), they fish amber. In about 600 years BC
Ezekiel describes king Tyre’s clothing decorations, and mentions amber jewellery. Amber is very often mentioned in Greek literature. Amber is mentioned even in the 10th century BC in Assyrian cuneiform. It says that in the sea, where Northern winds are changing (Persian
Gulf), his (king’s) merchants gather pearls, and in the sea, where
Northern Star shines (Baltic), they fish amber. In about 600 years BC
Ezekiel describes king Tyre’s clothing decorations, and mentions amber jewellery. Amber is very often mentioned in Greek literature. |
1-10 11-17


